
This was an arithmetic logic unit you sit back and admire. It was part of Honeywell's Datamatic 1000 computer. (Image courtesy of Honeywell, Inc.)
Thirty Years Later
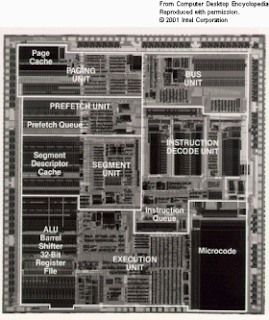
The ALU embedded within this 386 chip would fit on the end of a pencil eraser with room to spare. (Image courtesy of Intel Corporation.)
In computing, an arithmetic logic unit (ALU) is a digital circuit that performs arithmetic and logical operations. The ALU is a fundamental building block of the central processing unit (CPU) of a computer, and even the simplest microprocessors contain one for purposes such as maintaining timers. The processors found inside modern CPUs and graphics processing units (GPUs) have inside them very powerful and very complex ALUs; a single component may contain a number of ALUs.
Mathematician John von Neumann proposed the ALU concept in 1945, when he wrote a report on the foundations for a new computer called the EDVAC.

A typical schematic symbol for an ALU: A & B are the data (registers); R is the output; F is the Operand (instruction) from the Control Unit; D is an output status.
2 comments:
Great!So informative
Thanks for your comment.
Post a Comment